The healthcare sector is currently undergoing a period of significant innovation. Technological advancements are influencing various aspects of the industry, including security, predictive capabilities, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
When discussing the positive changes brought about by technology in healthcare, we frequently mention concepts such as blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). Even Software as a Medical devices (SaMD) are gaining prominence. However, the foundational element that supports all these next-generation technological breakthroughs is cloud computing. This technology represents a long-standing trend that continues to shape the future of the healthcare sector.
Cloud computing has caused a significant transformation in how medical data is generated, utilized, stored, and shared within the healthcare field. Starting from the era of traditional storage methods to the current state of complete digitization of healthcare data, the industry has made substantial progress in enhancing data management strategies.
In this article, we will delve into various aspects of cloud computing's impact on healthcare and its transformative influence on the field.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud computing in the healthcare sector refers to the method of utilizing internet-based remote server access to store, manage, and process healthcare-related information. This stands in contrast to the traditional approach of setting up on-site data centers on personal computers to host data. This alternative approach offers healthcare stakeholders the flexibility to access hosted data on remote servers.
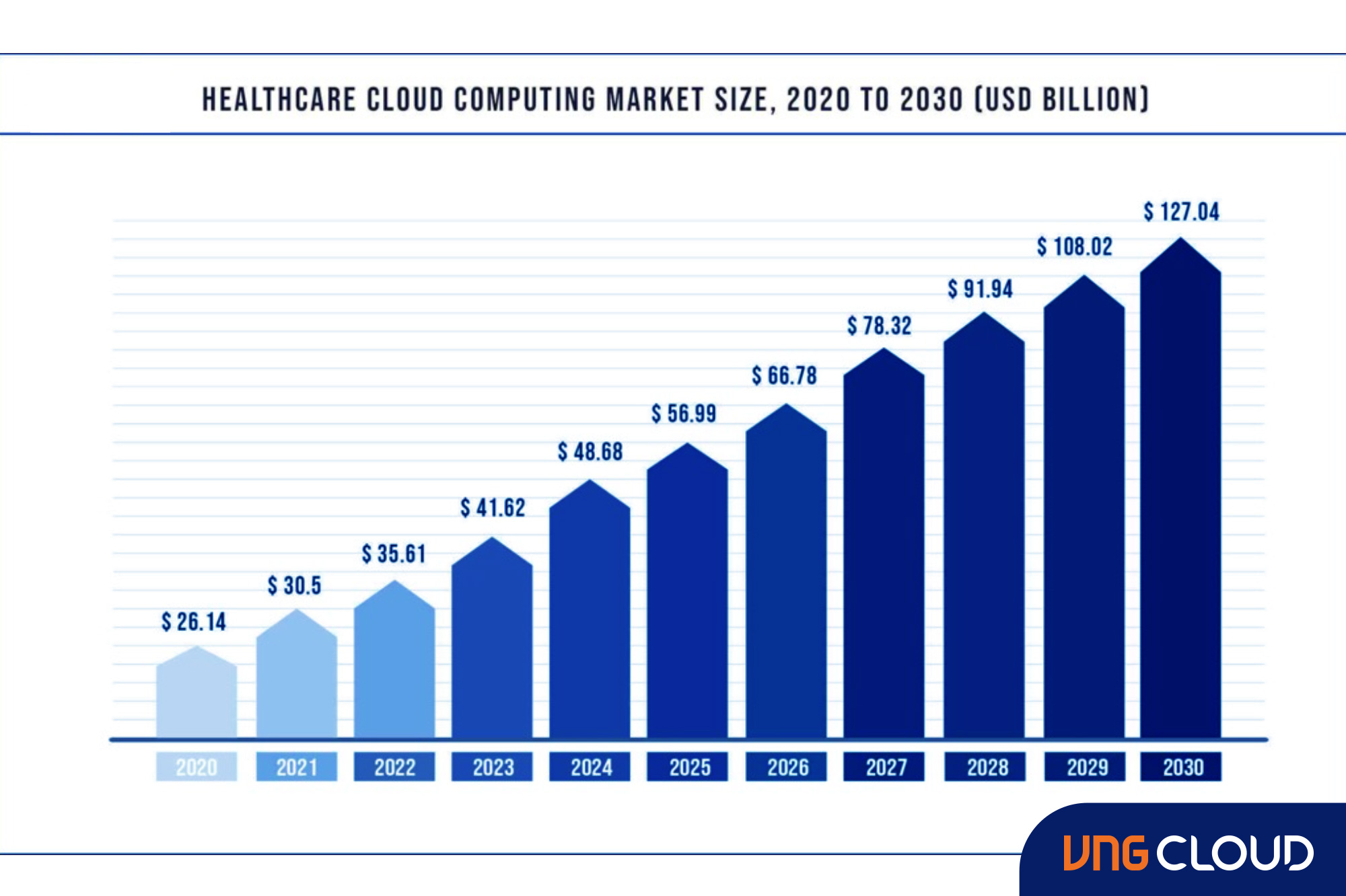
As indicated by a report from BCC, the global market for healthcare cloud computing is projected to reach $35 billion by 2022, demonstrating an annual growth rate of 11.6%.
Transitioning to cloud technology offers dual advantages for both patients and healthcare providers. From a business perspective, virtualization within cloud computing has demonstrated its value by reducing operational costs and empowering healthcare providers to offer top-tier, individualized medical care.
Conversely, patients are becoming accustomed to the immediate availability of healthcare services. Furthermore, healthcare cloud computing enhances patient engagement by granting them access to their medical data, leading to improved patient outcomes.
The ability to access healthcare remotely, combined with real-time data sharing and synchronization, dismantling geographical barriers to healthcare accessibility.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry?
The healthcare sector is ever-changing, with technology now crucial for improved patient care. A prominent recent tech development is cloud computing, reshaping healthcare. Cloud solutions offer healthcare institutions numerous advantages: scalability, security, compliance, swift recovery, collaboration, cost reduction, patient experience enhancement, innovation, remote monitoring, population health management, and accessibility.
1. Enhanced Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing empowers healthcare institutions to swiftly and effortlessly expand their IT infrastructure, avoiding costly hardware and software updates. This flexibility also enables healthcare providers to manage higher patient loads, and extend services to new areas without substantial capital investments.
2. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Cloud computing delivers elevated data security and compliance features vital to healthcare. Storing data in secure, external centers safeguards sensitive patient information from cyber risks and breaches. Moreover, cloud-based solutions aid healthcare providers in adhering to stringent data privacy mandates like Decree 13/2023/ND-CP and other regulatory requirements.
3. Faster Disaster Recovery
Should a disaster or system failure occur, healthcare institutions must swiftly restore crucial data and systems. Cloud computing grants healthcare providers the capability to rapidly recover, guaranteeing uninterrupted patient care. Through cloud-based disaster recovery solutions, healthcare organizations can reinstate critical data and systems within minutes, significantly reducing downtime.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Cloud computing empowers healthcare institutions to foster more efficient collaboration and communication, both internally and with external collaborators. Cloud-based solutions ensure secure, instantaneous access to patient data and vital information, facilitating seamless cooperation among healthcare providers to enhance patient care delivery.
5. IT Cost Savings
Cloud computing offers healthcare institutions a means to decrease IT expenses by removing the necessity for costly hardware and software updates. Through cloud-based solutions, healthcare providers can pay solely for the required computing resources when needed, sidestepping for expensive capital investments.

6. Enhanced Patient Satisfaction
Cloud computing has the potential to enhance patient satisfaction by granting healthcare providers immediate access to patient data and vital details. Equipped with current patient information, healthcare providers can render well-informed decisions regarding patient care, thereby delivering superior and more tailored medical services to patients.
7. Increase Flexibility and Innovation
Cloud computing empowers healthcare institutions with greater agility and innovation by granting access to cutting-edge technologies and software applications. Through adoption of cloud-based solutions, healthcare providers can swiftly and effortlessly experiment with new technologies and software applications, bypassing the requirement for substantial capital expenditure. This accelerates innovation within healthcare, leading to improved patient care delivery.
8. Improved Monitoring of Remote Patients
Cloud computing has the potential to enhance remote patient monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to offer superior care to patients in their homes. Through cloud-based solutions, real-time data on patient vitals and crucial details can be accessed, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients more efficiently and respond promptly to potential concerns.
9. Enhanced Management of Population Health
Cloud computing offers the potential to enhance population health management for healthcare institutions through immediate access to patient data and vital information. Equipped with current patient information, healthcare providers can identify potential health concerns and intervene proactively, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and curbing healthcare expenses.
10. Better Accessibility
Cloud computing offers healthcare organizations increased accessibility to vital patient data and other essential information. With cloud-based solutions, healthcare providers can retrieve patient data and other pertinent information from any location and at any time, as long as an internet connection is available. This capability empowers healthcare providers to access patient data and essential information while on the move, enabling them to provide improved care and make well-informed decisions regarding patient well-being.

Cloud FAQs in Healthcare
1. How is cloud computing integrated into healthcare systems?
Cloud computing furnishes healthcare organizations with a secure infrastructure that enhances the scalability and flexibility of data management systems. The core functionalities underpinning cloud services in healthcare encompass authorization, authentication, data persistence, data confidentiality, and data integrity. The ensuing steps outline the operational mechanics of cloud computing within a healthcare setting:
- Patients request authorization from the public cloud server, which is relayed to the private cloud server.
- The authorization request is verified and either accepted or rejected.
- Physicians ask for data access authorization.
- Upon approval, physicians access cloud-stored data.
- Physicians provide patients with medical guidance using accessed data.
2. What are the top applications of cloud computing in healthcare?
Here are several cloud computing applications in healthcare, contributing to a technology-driven healthcare ecosystem:
- Drug discovery and telemedicine;
- Management information system;
- Digital libraries;
- Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS);
- Virtual medical universities;
- Enhanced practice management;
- Population health management;
- Biological software;
- Health education.
3. What are the security challenges of cloud computing in healthcare?
Key security challenges of cloud computing in healthcare include: access control, identity management, network security, authentication, internet-based access, authorization, and vulnerability to cyber-attacks, highlighting significant concerns about security and privacy.
VNG Cloud complies with the international information security standard ISO 27017. Moreover, products such as vServer and vStorage are integrated with IAM - Identity and Access Management solutions across all resources and services of VNG Cloud. This enables the initiation of security rules to manage resources from users, to businesses, and to various roles and positions.
4. Are there obstacles to integrating cloud computing into healthcare?
Several challenges exist when implementing cloud computing in healthcare:
- Shortage of skilled specialists: A primary hurdle involves acquiring proficient software developers who can collaborate effectively with healthcare organizations.
- Security concerns: Embracing the cloud in healthcare systems may raise privacy issues for medical professionals, potentially leading to data breaches and inadequate network security.
- Functional limitations: Cloud computing alone might not suffice. Building a robust analytics framework often necessitates smart connected devices and comprehensive master data management systems.
5. What is the vision of cloud computing in healthcare?
With ongoing digital advancements, healthcare entities are swiftly adopting cloud infrastructure for data management and patient records. Cloud computing also facilitates the integration of AI into healthcare.
The future entails seamless interoperability between medical devices and healthcare systems, ensuring secure data sharing and streamlined operations.
Today, businesses of all sizes utilize the cloud for various purposes including disaster recovery, data backup, virtual desktops, email, software development, testing, and big data analytics.
Cloud computing relies on virtualization – technology that manipulates hardware through software, ultimately supporting the delivery of cloud services.