A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a secure and isolated Private Cloud that operates within a Public Cloud infrastructure. In a VPC, customers can execute code, store data, host websites, and perform other tasks typical of a Private Cloud environment. However, unlike traditional Private Cloud, a VPC is remotely hosted by a Public Cloud provider. This setup combines the scalability and convenience of Public Cloud computing with the data isolation provided by Private Cloud environments.
To illustrate, envision a Public Cloud as a bustling restaurant, while a virtual Private Cloud is akin to a reserved table within that restaurant. Despite the restaurant being crowded with patrons, a table marked as "Reserved" is exclusively available to the party that booked it. Similarly, in a Public Cloud environment where multiple customers access computing resources, a VPC allocates a portion of those resources exclusively for the use of a single customer.
What is a Public Cloud? What is a Private Cloud?
Public Clouds are externally managed platforms that follow the standard cloud computing model to provide resources and services to remote users. Within Public Clouds, customers share resources with other tenants, commonly accessing virtual machines (VMs), applications, or storage. These resources can encompass databases, firewalls, load balancers, management tools, and other Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Software as a Service (SaaS) components.
The technical term for this arrangement, where multiple distinct customers access the same cloud infrastructure, is "multi-tenancy”.
In contrast, a Private Cloud is single-tenant, exclusively offered to a single organization. Operating as single-tenant computing infrastructures, Private Clouds ensure that organizations utilizing them do not share resources with other users. Thus, A VPC, although it exists within a Public Cloud environment, ensures that no other entity shares the VPC with the designated customer.

How a VPC works
In a VPC setup, the provider ensures that each customer's data is securely isolated from others, both during transit and within the provider's network. This involves implementing security policies that may include assigning unique VLANs or offering subnets/VPNs to customers.
- Subnets: A subnet defines a specific range of IP addresses within a network, reserved for private use and inaccessible to others within the network. In a VPC, these are private IP addresses that aren't accessible via the public Internet, unlike typical publicly visible IP addresses.
- VLAN: A LAN, or Local Area Network, comprises interconnected computing devices without internet access. A VLAN, a virtual LAN, partitions a network at a different layer in the OSI model (layer 2 instead of layer 3), akin to subnets.
- VPN: A VPN encrypts data to create a private network over a public one. Though VPN traffic traverses public Internet infrastructure, it's encrypted and hidden from view.
Within a VPC, a dedicated subnet and VLAN are reserved exclusively for the customer, preventing others in the Public Cloud from accessing resources within the VPC. The customer connects to their VPC via VPN, ensuring data privacy from other Public Cloud users.
Some VPC providers offer further customization options:
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Maps private IP addresses to public ones for connections to the public Internet, and vice versa. This enables hosting public-facing websites or applications within a VPC.
- BGP route configuration: Allows customers to customize BGP routing tables to connect their VPC with other infrastructure.
Features of VNG Cloud’s VPC
VPCs allow enterprises to access the advantages of Private Clouds, such as enhanced network control, while using Public Cloud resources in a flexible Pay-as-you-go model.
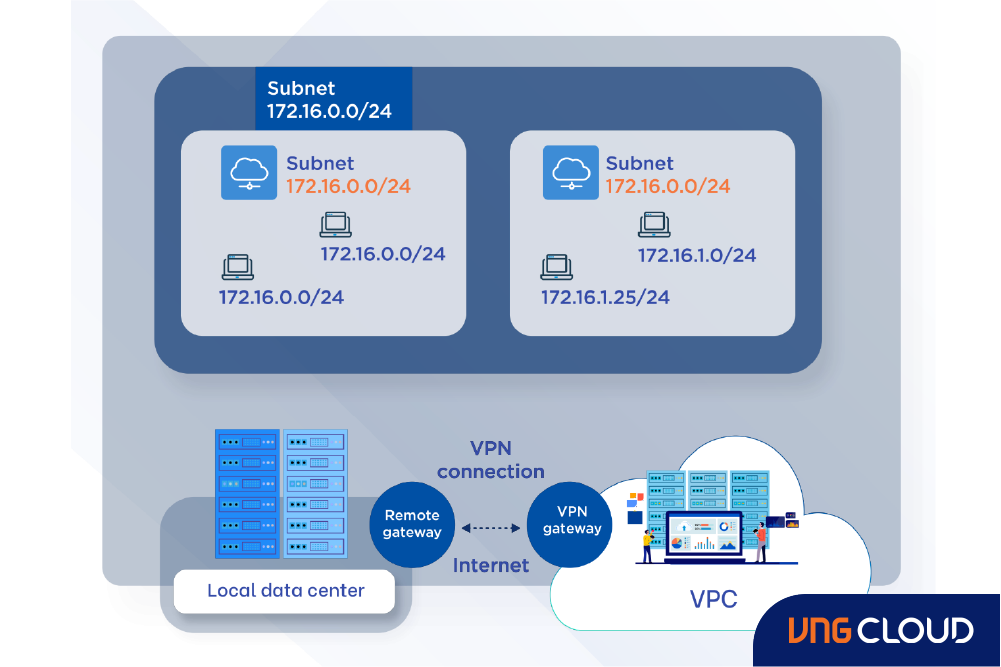
On VNG Cloud’s infrastructure, VPC Network and Security Groups enable customers to easily initialize networks and have peace of mind knowing that VMs are protected on multiple levels.
- VPC Network: Allow customers to self-create networks (CIDR) based on their pre-planned application needs.
- Security Groups: Functionality designed to safeguard individual VM or clusters of multiple VMs using customer-defined and authorized policies. Security Groups’ Rule includes: Name, Description, Rule, Protocol, Port | Range Port, and CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing).
Using VNG Cloud's VPC offers organizations the following advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Our VPCs offer network isolation and customizable security, safeguarding resources from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Data Compliance: VNG Cloud ensures data compliance through strong security measures and adherence to industry regulations, such as Decree 53/2022/ND-CP and Decree 13/2023/ND-CP.
- Cost Efficiency: With Pay-as-you-go model, you can remove the need for substantial upfront hardware investments and lowering infrastructure costs.
- Scalability: Easily adjust your infrastructure to changing demands, optimizing resource allocation and saving costs.
- High Availability: VNG Cloud’s VPCs offer built-in redundancy and failover for application availability and reduced downtime.
- Network Segmentation: Our VPCs allow you to organize your resources into multiple subnets, improving resource management and data separation.
VNG Cloud’s VPCs offer users a range of network services, including DHCP, Route Table, Internet Gateway, Floating IP, External Interface, Load Balancing, VPN Gateway, and more. You have complete control over your VPC, enabling you to define different subnets, configure route tables, and manage gateways according to your needs. Whether they are on-premises workloads or VMware workloads, you can seamlessly transition to our VPC environment while maintaining absolute security for your critical data. For more details, please visit this link or contact us for technical advice.