Cloud & AI - Scalable and Secure for You
Access a full portfolio of Compute, Storage, and AI services - optimized to work together seamlessly, backed by modern infrastructure, expert support, and end-to-end compliance.
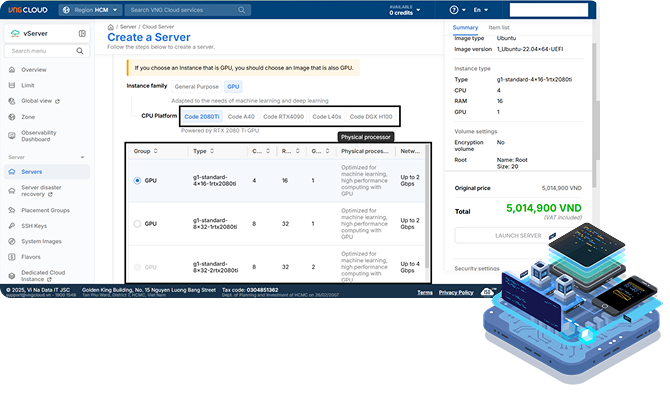
GPU Cloud
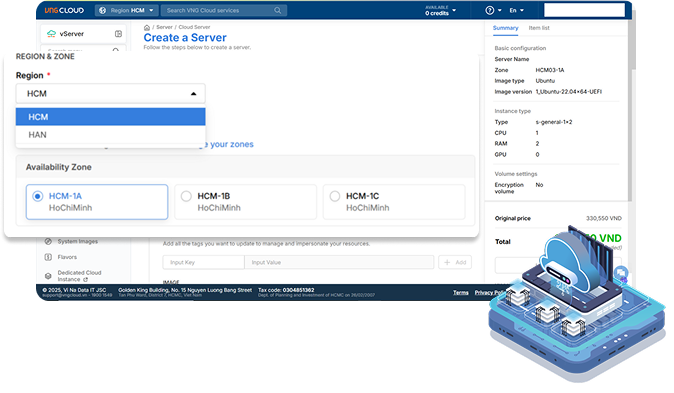
vServer
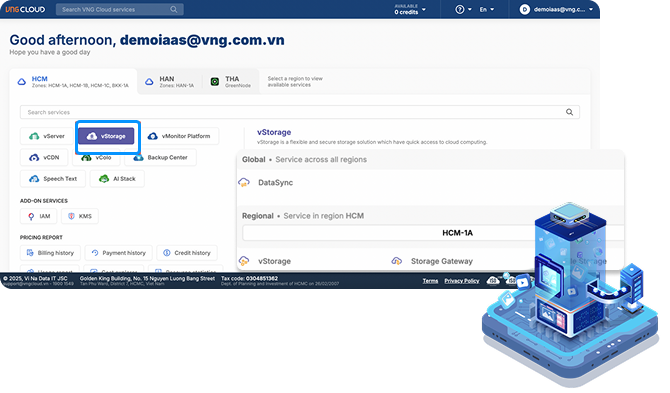
vStorage
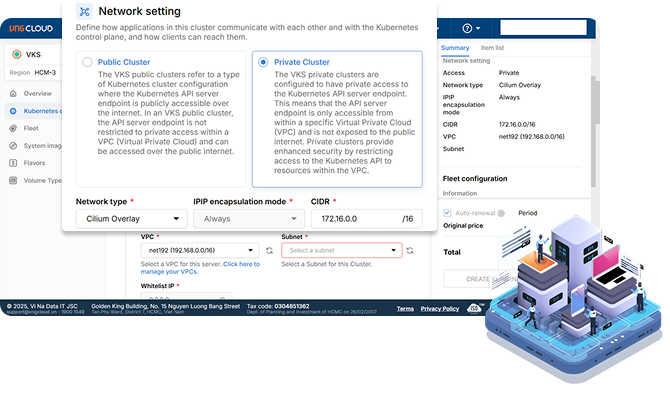
VKS (Kubernetes)
vCDN
Comprehensive Solutions Tailored for Every Industry
Whether you're launching new digital services, modernizing systems, or deploying AI applications, VNG Cloud delivers industry-grade performance, security, and in-depth technical support.
Financial services & Fintech
Ensure a highly available and resilient infrastructure for digital solutions and AI adoption
Retail & E-commerce
Edtech
SaaS & Tech startup
Everything You Need to Build, Run, and Scale with Cloud & AI
From infrastructure to compliance, AI training to app delivery—VNG Cloud gives you the tools, trust, and technical depth to move fast and securely.
Continuous Innovation that Keeps You Ahead
Deliver new capabilities faster with continuous updates, performance enhancements, and service expansion.
Modern AI at Scale, Built on NVIDIA Infrastructure
Power your AI models with NVIDIA® H100, L40S, A40 - optimized for both training and inference.
Managed Services & vMarketplace Ecosystem
Accelerate deployment with ready-to-use services and a growing ecosystem of AI, DevOps, and data tools.
Expert Support from Day 1 to Scale up
Work with cloud-certified architects and engineers—ready to support your mission from pilot to production 24/7.
Compliance-first Cloud, Built for Vietnam
Ensure data sovereignty and meet industry regulatory standards with PCI-DSS, ISO 27017/18, and local hosting.