A. Overview of technology application in Logistics in Vietnam
The global economy's robust growth and diverse international connections have driven significant advancements in logistics. In this context, the application of information technology plays a crucial role in enhancing the competitive capabilities of businesses, especially logistics enterprises. Therefore, logistics companies increasingly need to focus on researching, implementing, and developing information technology in their management activities.
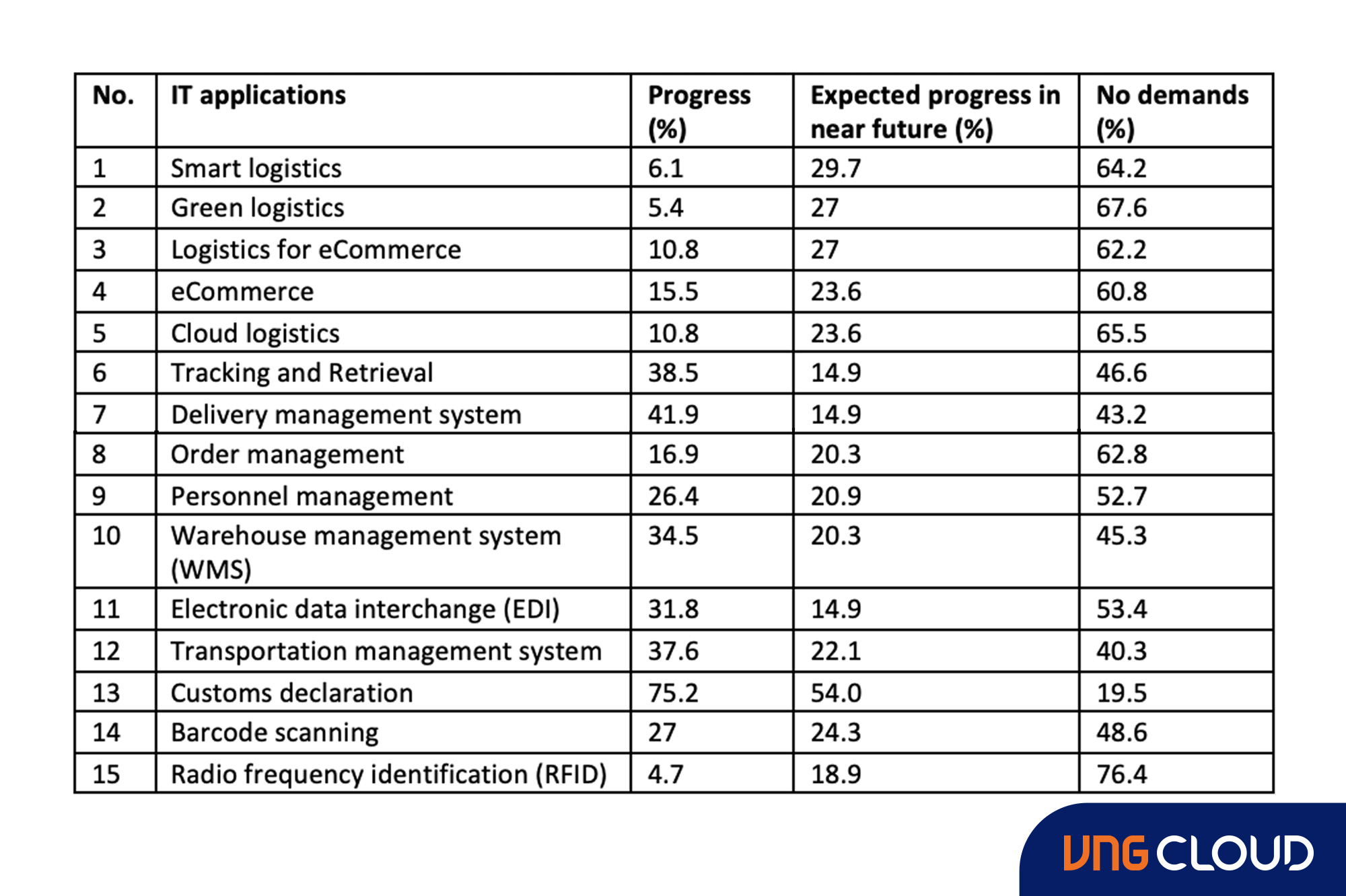
Currently, logistics companies in Vietnam offer a range of 2 to 17 different logistics services, mainly focusing on freight forwarding, transportation, warehousing, express delivery, and customs declaration. Approximately 50-60% of these companies have adopted various types of technology, depending on their scale and service characteristics. However, financial capability remains a significant challenge for logistics enterprises in implementing information technology.
According to the analysis by members of the Vietnam Logistics Business Association (VLA), only a few services, such as customs declaration, comply with over 75.2% of the mandatory requirements for electronic customs declaration. Other information technology applications fall below the average level. For instance, the shipment management system reached 41.9%, tracking and tracing achieved 38.5%, the transportation management system stood at 37.6%, barcode scanning reached 27%, and personnel management attained 26.4%.
Analysis of the technology application level among VLA members also shows that only a few services, such as Order Management, reached 16.9%; E-commerce attained 15.5%, and Logistics for e-commerce reached 10.8%. This clearly reflects the limitation of information technology applications in logistics enterprises in Vietnam, as it cannot fully meet the development needs and current trends. Moreover, the level of application of sustainable information technology, such as Smart Logistics and Green Logistics, is very low, at 6.1% and 5.4%, respectively, indicating that logistics enterprises need to make more efforts in applying information technology and digital transformation. The expectation of achieving 50% information technology application in the future requires significant efforts and commitment from businesses.
Vietnam's logistics sector has currently implemented information technology in four main areas:
- Road transportation: Utilizing technology applications to optimize vehicle capacity, route planning, and control, aiming to increase the rate of fully loaded cargo trucks.
- E-commerce warehousing: Applying automation solutions in warehouse management for e-commerce, last-mile delivery, and express delivery.
- Manufacturing: Combining automated operations with lean manufacturing principles to enhance operational efficiency.
- Supply chain management: Some domestic retailers are deploying integrated applications of information systems, automation, and artificial intelligence to manage the supply chain from procurement to distribution and end consumers.
According to a survey by Vietnam Report, in the past year, 100% of logistics businesses have increased investment in digital transformation, with 86% of them expecting significant benefits in productivity and business efficiency from the application of technology, digitization, and digital transformation in the future. Furthermore, 36% of logistics companies believe that incorporating technology into their logistics processes will enhance the global customer experience. Approximately 68% of companies have already implemented advanced technology applications of the Industry 4.0 revolution in their business operations, including the Internet of Things (86%), cloud computing (82%), artificial intelligence (45%), Big Data, and blockchain (42%).
B. How Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Logistics transforms the Supply Chain
Supply Chain Management (SCM) in the Industry 4.0 era, along with 4.0 Logistics, stands as one of the most influential industries in the global economy, particularly in the present landscape with a significant surge in e-commerce. The emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Logistics has driven growth across various service sectors, including Logistics. AI in Logistics has ushered in the era of "digital transformation" by seamlessly integrating, automating, and streamlining operational processes, resulting in substantial cost and time savings.
1. 4.0 Logistics: A new era

The American Council of Logistics defines Logistics as the process of planning, organizing, implementing, and controlling the cost-effective movement and storage of raw materials, semi-finished and finished products, along with relevant information, from production to final consumption, with the coordination of human forces and machines to meet customer requirements.
In this competitive Logistics market, technology serves as a significant competitive advantage. 4.0 Logistics focuses on harnessing new and innovative technologies, such as paperless transportation order processing with electronic waybills. AI in Logistics has revolutionized the industry with its capabilities in:
- Automatic identification.
- Real-time location tracking.
- Internet of Things (IoT).
- Big Data processing in real-virtual networks.
- Internet of Business (IoB) or eBusiness.
4.0 Logistics amalgamates cutting-edge technologies for a more streamlined operation, including GPS, Barcode, Data Matrix code, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Internet, and Telecommunications, as well as On-Premises and Cloud software. These technological advancements have brought remarkable benefits to Logistics vendors:
- Reduction of unnecessary expenses.
- Automation of repetitive tasks.
- Improved forecast accuracy.
- Ensured product quality.
- Real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities.
- Enhanced transportation services.
- Facilitated advanced decision-making processes.
AI in Logistics, based on the Internet of Things and Big Data, can address labor and transportation vehicle challenges that have long troubled logistics vendors.
2. How has AI in Logistics changed the way supply chains operate?

AI in Logistics has revolutionized the way supply chains operate, bringing about significant breakthroughs in the 4.0 technology era. Three key applications of AI in Logistics stand out:
2.1. Demand forecasting
The logistics industry heavily relies on data, and the rapid development of data has become a crucial aspect of its operations. Amazon's success serves as a prime example of the importance of Big Data in business strategy. By analyzing data from over 152 million customers, Amazon gained insights into purchase behaviors, allowing them to recommend relevant products based on purchase history and personal preferences.
However, effectively harnessing these data sources has been a challenge for logistics planners, as manual procedures for data observation, capacity estimation, and network analysis are time-consuming and may not yield optimal delivery routes in real time. AI in Logistics, on the other hand, can perform these tasks accurately within seconds. By incorporating more accurate data and relevant external factors into the calculations, AI can better estimate upcoming demand.
DHL serves as a prime example of AI's impact on logistics operations. Their management system tracks over 8 million online and social media posts using Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to detect potential issues in the supply chain. Through automated data extraction, DHL can identify material shortages, access issues, and supplier statuses, enabling them to stay ahead of upcoming challenges and avoid unnecessary additional costs.
2.2. Automation in transportation and delivery using robots
AI in Logistics has significantly increased automation in the entire delivery process, including order tracking, inventory management, product control, distance optimization, and real-time fleet management.
- Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV): The use of AGVs and autonomous mobile robots has become more prevalent. AGVs can move within the warehouse without human guidance, improving delivery efficiency, saving time, and ensuring the safety of goods during transportation.
- Robots: The growing need for quick, flexible, and efficient operations has led to a surge in the use of robots in logistics. Robots can replace human labor in various warehouse operations, such as receiving, warehousing, warehouse management, order processing, and shipping.
- Drones - Unmanned delivery aircraft: Drones have gained popularity worldwide as a means of delivering packages. Programmed to deliver packages to specified locations in the most efficient route, drones save time, and transportation costs, and reduce errors compared to traditional shipping.
According to surveys conducted by VTI (2022), AI in Logistics has reduced last-mile delivery costs by 14% and increased the number of goods delivered per vehicle by 13%.
2.3. Smart warehouses
In the Industry 4.0 era, warehouses are now operating automatically with the integration of AI and IoT, connecting various IoT devices such as IoT shelving and monitoring systems for ventilation, cooling equipment, and more. This ensures goods preservation, security monitoring, fire and explosion prevention, and other safety measures. Additionally, goods-handling machinery and equipment are automated and integrated with the network system. The increasing use of IoT applications plays a crucial role in this era.

Smart warehouses offer several outstanding advantages, including:
- Smart warehouse management with safe and easy automated operations.
- High stability and low operation costs.
- Flexible control, meeting customer requirements effectively.
- Significant increase in storage capacity.
AI in Logistics provides automation at every stage of warehousing by utilizing a network of connected IoT devices. These devices are connected via the internet and operated through command changes, allowing the Logistics algorithm to optimize warehouse operations such as receiving, put-away, and picking. Smart warehouses also offer special modes for goods preservation, such as cooling, ventilation, and protection against sunlight. Additionally, they are equipped with measures to prevent fire, explosion, electrical leakage, and illegal intrusion.
Moreover, smart warehouses are supported by other simple yet effective solutions for internal traffic systems, including pallet conveyor systems and roller conveyors. In the future, warehouses are expected to be specifically designed for machines that can work 24/7 without the need for human supervision.
3. Utilize AI in Logistics operations today with VNG Cloud
VNG Cloud offers comprehensive software development solutions with expertise in AI, aimed at facilitating digital transformation and promoting business growth.

In the logistics industry, precise planning and flexible coordination among suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders are crucial. With cloud computing, logistics vendors can enhance inventory management and accurately forecast demand and supply. This enables them to analyze data effectively and make well-informed plans, optimizing the distribution of goods and maintaining a balanced supply and demand.